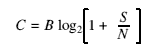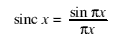
56K Modems
Definitions
- Analogue to Digital Converter (ADC)
- An electronic device which converts an analogue signal into a digital representation. At regular intervals, the ADC samples the analogue waveform, quantises it, and outputs a digital value. The important specifications for an ADC are its resolution and its sampling rate. The resolution, measured in bits, represents the accuracy with which the device can digitise the analogue signal. The sampling rate, measured in samples/s, represents the speed of the converter, and therefore the maximum frequency signal it can process.
- Bandwidth
- Of a signal: The band of frequencies occupied by the signal, measured between the frequencies at which the signal is half its maximum power.
Of a channel: The band of frequencies which may be transferred down the channel, measured between the frequencies at which the channel loss is twice its minimum.
- Carrier
- A signal used to carry information down a channel. The carrier is modulated with the information to be transferred. A carrier is often used to transfer information down a channel which would otherwise be unable to carry the raw data.
- Channel
- A generic term for the medium through which a signal is carried. May be wire (eg. a telephone channel), optical fibre (eg. cable television), the air (eg. radio), or a combination of several media.
- Companding
- A contraction of compressing and expanding. This process reduces the quantisation noise added to a voice signal, by using closely spaced levels for small signals and wider spaced levels for large signals. This allows the predominantly quiet human voice to be sampled more accurately, reducing the error and therefore the quantisation noise. A voice signal is expanded before being carried over the digital network, then compressed when it returns to the analogue line.
- Digital Signal Processor (DSP)
- A special class of microprocessors, dedicated to performing repetitive but complex calculations on a stream of data. DSPs are optimised to run a limited number of mathematical operations at high speed. They are often used to process analogue signals, taking their input from Analogue to Digital Converters, or sending their output to Digital to Analogue Converters.
- Digital to Analogue Converter (DAC)
- An electronic device which converts a digital value into an analogue signal. At regular intervals, the DAC reads in digital data and outputs an analogue representation. A DAC is specified by its resolution and sample rate. The resolution, measured in bits, determines the accuracy of the analogue signal generated. The sample rate, measured in samples/s, determines the speed of the device, and the maximum frequency it can generate.
- Equalisation
- Measuring the characteristics of a channel in order to compensate for them. Typically the loss, time delay and bandwidth are measured. The transmitter and receiver can then make adjustments to improve the received signal.
- Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN)
- A digital telephone system. Basic Rate ISDN (BRI) comprises two 64 kbit/s telephone or "Bearer" channels, and a single 16 kbit/s signalling or "Data" channel. Primary Rate ISDN (PRI) comprises sixteen 64 kbit/s Bearer channels, and one 64 kbit/s Data channel.
- Inter-Symbol Interference (ISI)
- When symbols are transmitted through a channel, they become 'blurred' in time. This causes the end of one symbol to overlap the beginning of the next, resulting in corruption of the data. Hence, interference between symbols.
- Internet Service Provider (ISP)
- Companies providing access to the Internet. They are anticipated to be the main user of the 56 kbit/s systems.
- Modulation
- Modifying a carrier with an information signal, either analogue or digital, with the aim of transmitting the carrier and recovering the information at the destination.
- Noise
- Any unwanted signal. It may be natural, such as thermal noise, or man-made, such as crosstalk. The latter form is also known as Interference, but it may be considered to be noise as it has a similar effect on the communications system.
- Quantisation
- Part of the process of converting an analogue signal to a digital signal. After quantisation, the analogue amplitude is represented by the nearest discrete level, or binary number.
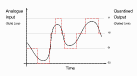 An Analogue-to-Digital Converter (ADC) quantises its input signal to produce a digital output. For example, an 8 bit ADC uses 256 discrete levels. Quantisation should not be confused with Sampling; the latter is an operation on time, whilst the former is an operation on amplitude.
An Analogue-to-Digital Converter (ADC) quantises its input signal to produce a digital output. For example, an 8 bit ADC uses 256 discrete levels. Quantisation should not be confused with Sampling; the latter is an operation on time, whilst the former is an operation on amplitude.
- Quantisation Noise
- When an analogue signal is quantised, some accuracy is lost due to the conversion from a continuous signal to one with, for example, only 256 possible levels. This conversion error is often considered to be a form of noise, as it has a similar effect on the signal quality.
- Sampling
- Part of the process of converting an analogue signal to a digital signal. At regular intervals, the analogue amplitude is measured and then held constant until the next measurement. The point at which the waveform is measured is known as the sampling instant.
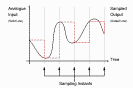 An Analogue-to-Digital Converter (ADC) samples its input signal to produce a digital output. For example, the ADCs in the telephone exchange operate at a rate of 8,000 samples/s. Sampling should not be confused with Quantisation; the latter is an operation on amplitude, whilst the former is an operation on time.
An Analogue-to-Digital Converter (ADC) samples its input signal to produce a digital output. For example, the ADCs in the telephone exchange operate at a rate of 8,000 samples/s. Sampling should not be confused with Quantisation; the latter is an operation on amplitude, whilst the former is an operation on time.
- Shannon's Limit
- Describes the maximum possible data transfer rate through a channel, given its bandwidth, and the ratio of signal power to noise power.
- Signal to Noise Ratio
- The power of the wanted signal, divided by the power of the noise. A critical measure of channels and communication systems. If the signal to noise ratio falls too low, the signal will not be recoverable.
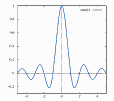
- sinc(x)
- A signal shape commonly encountered in communications. It represents the ideal received signal when a fast pulse is transmitted through a limited-bandwidth channel.
- Symbol
- The unit of transmitted data. One symbol may represent more than one data bit . Now commonly used as a measure of transmission rate - symbols per second - replacing the term "baud". As an example of its use, the 16-QAM modulation scheme encodes 16 bits per symbol.
- Synchronisation
- Adjusting the timing of the receiver's clock so that it exactly matches the incoming data. No separate clock signal is transmitted, so the receiver must extract the timing information from the received data. This is often done during a training sequence, at the beginning of a connection.
Contents
Main Index - Articles Index
Other interesting websites
 An Analogue-to-Digital Converter (ADC) quantises its input signal to produce a digital output. For example, an 8 bit ADC uses 256 discrete levels. Quantisation should not be confused with Sampling; the latter is an operation on time, whilst the former is an operation on amplitude.
An Analogue-to-Digital Converter (ADC) quantises its input signal to produce a digital output. For example, an 8 bit ADC uses 256 discrete levels. Quantisation should not be confused with Sampling; the latter is an operation on time, whilst the former is an operation on amplitude.
 An Analogue-to-Digital Converter (ADC) samples its input signal to produce a digital output. For example, the ADCs in the telephone exchange operate at a rate of 8,000 samples/s. Sampling should not be confused with Quantisation; the latter is an operation on amplitude, whilst the former is an operation on time.
An Analogue-to-Digital Converter (ADC) samples its input signal to produce a digital output. For example, the ADCs in the telephone exchange operate at a rate of 8,000 samples/s. Sampling should not be confused with Quantisation; the latter is an operation on amplitude, whilst the former is an operation on time.